Neuropathy in Hands Tips for Regaining Strength and Functionality
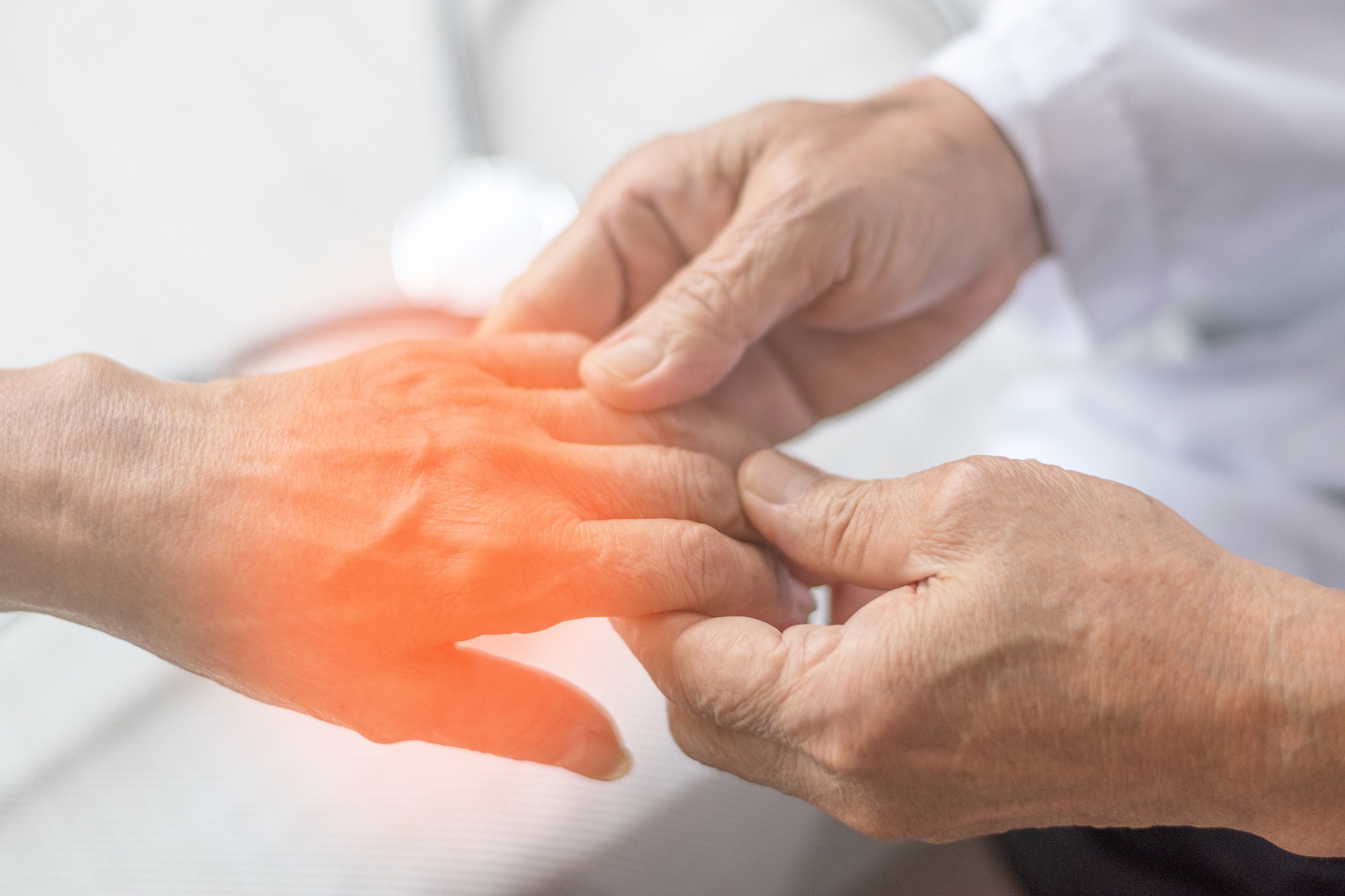
Neuropathy in the hands is a condition that can significantly affect a person’s quality of life. It often denotes tingling, numbness, weakness, or pain in the hands, making simple daily tasks challenging. While neuropathy can affect various parts of the body, focusing on your hands is crucial since they play a vital role in our daily activities.
How to know you have neuropathy in hands? Experiencing occasional hand or finger numbness and tingling sensations, possibly caused by an awkward sleeping position or the need to take a break from extended typing or gardening sessions. However, for some individuals, these “pins and needles” sensations signal a more significant issue – nerve damage and a condition referred to as peripheral neuropathy.
While this condition is treatable and not life-threatening, it’s essential to understand how it can be cured. The harshness of symptoms can range from mild inconvenience to disabling effects. Neuropathy in hands can affect not only the hands but also the legs, making it important to seek timely diagnosis and management to alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore neuropathy in hands, and discuss effective strategies to regain strength and functionality.
Identifying the Symptoms of Neuropathy in Hands and Legs
Peripheral neuropathy in legs and hands can manifest in various ways, and recognizing its symptoms is crucial for timely intervention. If you suspect neuropathy in your hands, you may encounter:
- Muscle Weakness
- Cramping and Twitching
- Difficulty Holding Objects
- Sensation of Wearing Gloves or Socks Unnecessarily
- Numbness, Prickling, or Tingling Sensations in the Hands
- Burning or Freezing Pain, Often Worse at Night
- Pain During Activities That Typically Don’t Cause Discomfort
Regardless of the intensity of these symptoms, peripheral neuropathy has a reputation for diminishing one’s ability to enjoy life’s activities and can even impede everyday tasks. Seeking prompt treatment from a qualified healthcare provider can significantly impact the management of your neuropathy symptoms.
Neuropathies often initiate their onset in the hands and feet, potentially resulting in any of the above manifestations. These conditions can affect a single nerve, multiple nerves, or numerous peripheral nerves throughout the body. There are three types of nerves involved each with its own specific functions and potential symptoms when affected by neuropathy.
Have a look:
- Sensory Nerves
These nerves facilitate the body’s reception of sensory information related to sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch. For instance, if you are experiencing neuropathy in your hands and fingers, you may struggle to discern the texture, temperature, or sharpness of objects. Sensory nerve damage typically leads to tingling, pain, and numbness.
- Motor Nerves
Motor nerves serve to transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord, controlling voluntary muscle movements. These nerves enable actions such as grasping objects, reaching, grabbing, and even the instinctive withdrawal from hot or cold stimuli.
- Autonomic Nerves
In contrast to the hands and fingers’ control, autonomic nerves oversee involuntary or semi-involuntary bodily functions, including breathing, heart rate, blood pressure regulation, digestion, bladder control, and perspiration. For example, individuals may experience variations in heart rate, difficulty swallowing, vomiting, or excessive sweating due to autonomic nerve involvement.
Identifying the specific type of neuropathy and its underlying causes is essential for tailored treatment and symptom management.
Factors Behind Neuropathy in Hands and Fingers
Damage to the nerves serving the upper extremities, whether caused by factors like overuse, injuries, autoimmune disorders, diabetes, or various other conditions, can lead to radiating pain in the hands and fingers. This pain often coexists with sensations of numbness, burning, or tingling, significantly impeding hand motion and functionality, and ultimately impacting one’s overall quality of life.
Common causes of this condition include:
Neuropathy in the hands and fingers can be attributed to various factors, each with its unique characteristics and implications. Recognizing these causes is vital for understanding and managing the condition effectively:
- Pinched Nerve: Nerve impingement in the hand can induce pain, numbness, and tingling. This can result from factors like injury and arthritis, with carpal tunnel syndrome being a common association. While it’s more prevalent in adults over 50, it can affect individuals of any age.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: This is the most common nerve compression disorder, affecting around 5% of the population. It tends to be more common in older adults and women. Chronic nerve inflammation leads to symptoms such as numbness, pain, and a burning sensation in the hand.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Peripheral neuropathy involves nerve damage outside of the brain and spinal cord. In the hands, it can manifest as muscle weakness, numbness, coordination loss, and pain. Various factors, including injuries, autoimmune disorders like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, and infections, can cause peripheral neuropathy.
- De Quervain’s Disease (De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis): Nerve damage in this condition results from inflammation of tendons in the hand and thumb. It occurs when the tendon sheath connecting the thumb and wrist becomes inflamed, leading to pain, weakness, swelling, and a sensation of “grating” in the wrist. Causes can include injury or repetitive hand movements that strain the thumb.
- Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb: These are variants of tendonitis affecting the index finger and thumb. A hallmark symptom is the catching or locking of the affected finger when trying to straighten or bend it. Conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, and repetitive stress injuries can cause trigger fingers.
- Dupuytren’s Disease (Dupuytren’s Contracture): This condition is characterized by abnormal thickening and hardening of hand tissue, causing nerve pain and severe functional limitations. When the tendons in the hand and palm are affected (known as palmar fasciitis), fingers can become bent and challenging to straighten.
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: It involves the compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow, resulting in tingling, numbness, and pain in the forearm, fingers, and impaired handgrip. This condition is sometimes misdiagnosed due to its similarities with other conditions and is typically caused by factors like bone spurs, arthritis, or previous fractures.
- Ganglion Cysts: These fluid-filled sacs can develop on the hands and wrists, potentially leading to nerve pain. While they are typically noncancerous and may resolve on their own, they can also exert pressure on nerves, affecting function and causing pain when they form in the joints, particularly the wrist.
- Osteoarthritis: The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis results from the gradual deterioration of joint cartilage due to aging and natural wear and tear. This process can cause inflammation, affecting hand nerves and disrupting their function, leading to stiffness and discomfort, which significantly limits hand mobility and function.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This autoimmune disorder mistakenly targets the joints, resulting in pain, stiffness, and swelling. It often leads to severe finger deformities and contributes to nerve pain in the hands.
Understanding the underlying cause of neuropathy in the hands is crucial for tailored treatment and effective symptom management.
Treating Nerve Pain in the Hands: Available Options
The approach to treating hand neuropathy varies depending on the individual case and the underlying condition. Pain management can often commence at home, while some cases may require medication, complementary therapies, or even surgical interventions. Treatment may involve a combination of these approaches, depending on the circumstances.
Lifestyle Treatment Options
The most helpful lifestyle treatment options include:
- Splinting: Wearing a splint can provide support and alleviate pressure on the affected area.
- Resting: Allowing your hands sufficient rest can prevent exacerbation of symptoms.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs can offer relief and reduce inflammation.
- Exercises and Stretches: Specific exercises and stretches may enhance hand mobility and strength.
- Medications: Pharmaceuticals can play a crucial role in managing nerve pain.
Prescribed Pharmaceuticals: Medications may include:
- While opioids like oxycontin and Percocet may be prescribed, it’s important to note that they are not intended for the treatment of chronic pain.
- Lidocaine patches, which deliver a topical anesthetic through the skin, can provide relief in peripheral neuropathy treatment.
- Anticonvulsant medications such as carbamazepine, Trileptal (oxcarbazepine), and Lamictal (lamotrigine) have demonstrated effectiveness in managing nerve pain.
Therapy and Procedures: When medication and at-home management do not provide adequate relief, several alternative options can be explored before considering surgery. These include:
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): TENS therapy uses electrical currents to alleviate pain and improve nerve function.
- Physical Therapy: Professional guidance and exercises can enhance hand strength and flexibility.
- Aspiration: This procedure involves the removal of excess fluid or tissue that may be compressing the nerve, providing relief.
The right treatment approach depends on the specific circumstances and the underlying cause of the nerve pain in your hands. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most suitable course of action for your condition.
Tips for Enhancing Strength and Functionality Despite Neuropathy in Hands
Living with neuropathy in the hands can be challenging, but there are practical strategies that can help improve hand strength and functionality:
Tip #1 – Physical Therapy for Hand Strength and Coordination: Work with a specialized physical therapist to develop a customized exercise regimen. These exercises can boost hand strength, enhance coordination, and improve dexterity. Regular practice of fine motor skills exercises is particularly beneficial for individuals with neuropathy.
Tip #2 – Occupational Therapy and Adaptive Techniques: Occupational therapists can teach you adaptive techniques to simplify daily tasks. They may suggest the use of assistive devices designed to make living with neuropathy in the hands more manageable. These strategies empower you to regain independence in your daily life.
Tip #3 – Effective Pain Management Strategies: Collaborate with a healthcare professional experienced in treating peripheral neuropathy. They can create comprehensive pain management plans that may include medications, nerve blocks, or other therapeutic interventions. Managing pain effectively can significantly enhance your quality of life and overall functionality.
Tip #4 – Nutrition for Nerve Health: Maintain a healthy diet rich in essential vitamins and nutrients, with a focus on B vitamins like B12. These vitamins are crucial for nerve health and function. Proper nutrition can contribute to an overall sense of well-being for those dealing with neuropathy.
Tip #5 – Lifestyle Modifications and Underlying Condition Management: Address and manage underlying conditions that may exacerbate neuropathy in the hands, especially if you have diabetes. Implement lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress reduction techniques. Avoid alcohol consumption and smoking, as these habits can worsen neuropathic symptoms.
Tip #6 – Exploring Holistic Approaches: Consider complementary holistic approaches to complement conventional treatments. Some individuals have reported relief and improved functionality through holistic health products like those offered by “Peripheral Neuropathy Treatments.” For example, devices such as the ReBuilder Medical device may provide additional support in managing neuropathy symptoms and promoting hand functionality.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily life, you can work towards regaining strength, functionality, and an overall improved quality of life while living with neuropathy in your hands.
Peripheral Neuropathy Treatments and the ReBuilder Device
“Peripheral Neuropathy Treatments” is a trusted source for holistic health products, with 17 years of experience in providing effective solutions to individuals seeking relief from neuropathy symptoms.
The ReBuilder Medical device, available through “Peripheral Neuropathy Treatments,” is a cutting-edge, FDA-cleared medical device specifically designed to stimulate and repair damaged nerves in the hands and feet. This innovative device utilizes electrical signals to replicate the body’s natural nerve impulses, which, in turn, promotes nerve regeneration and provides relief from neuropathy symptoms. It offers a non-invasive and drug-free approach, making it a valuable addition to your neuropathy management plan.
When you choose “Peripheral Neuropathy Treatments,” you gain access to a reputable brand dedicated to improving the lives of neuropathy patients. Explore the available options to begin regaining strength and functionality in your hands.